工厂模式是设计模式中比较基础也是比较常见的模式,一般用在创建对象上,所以属于创建型模式。工厂模式也分三种:简单工厂模式、工厂模式、抽象工厂模式。下面会对每个模式从解释、UML、代码进行详细说明
工厂模式
简单工厂模式
解释
简单工厂模式主要的意图就是抽象化实体类,让子类去决定实例化。
在小米加步枪时代,你需要一辆马车,你需要自己去创造。而在飞机大炮时代,你需要一辆汽车,你就会找工厂造一台,如果需求再变通一点,甲需要宝马,乙需要奥迪。所以造车的工厂就要能造两种车,而简单工厂模式就符合这种需求。这个优点就是调用者创建对象只需通过工厂创建,扩展性高
UML图
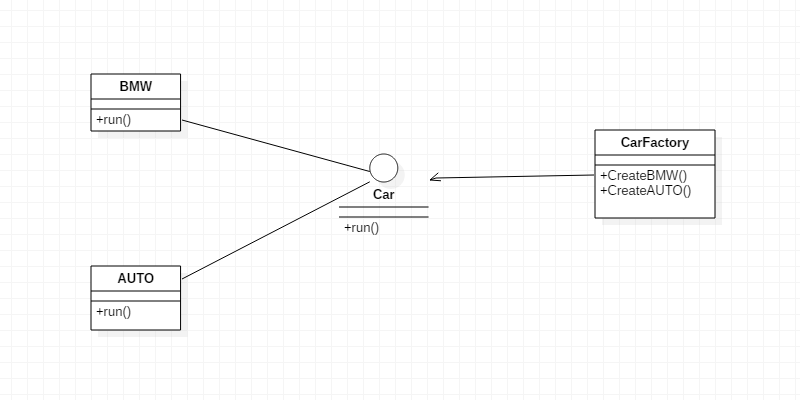
示例代码
Car接口基类1
2
3public interface Car{
void run();
}
BMW类1
2
3
4
5
6public class BMW implements Car{
public void run() {
System.out.println("BMW is run!");
}
}
AUTO类1
2
3
4
5
6public class AUTO implements Car{
public void run() {
System.out.println("AUTO is run!");
}
}
工厂类1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10public class CarFactory{
public static BMW CreateBMW() {
return new BMW();
}
public static AUTO CreateAUTO() {
return new AUTO();
}
}
具体调用1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9public class Test{
public static void main(String []args){
BMW bmw = CarFactory.CreateBMW();
bmw.run();
AUTO auto = CarFactory.CreateAUTO();
auto.run();
}
}
工厂模式
解释
工厂模式显然是对简单工厂模式的一种改进或者说是完善,遵循开闭原则。一个抽象工厂类派生出多个具体工厂类,具体工厂类只能生产对应的具体产品在现实需求中,宝马工厂和奥迪工厂肯定是不同的工厂,所以对工厂也进行抽象,这样就方便扩展了,当又来一种汽车时,只需要另外开辟一个工厂,而不要对原来工厂进行修改。
UML
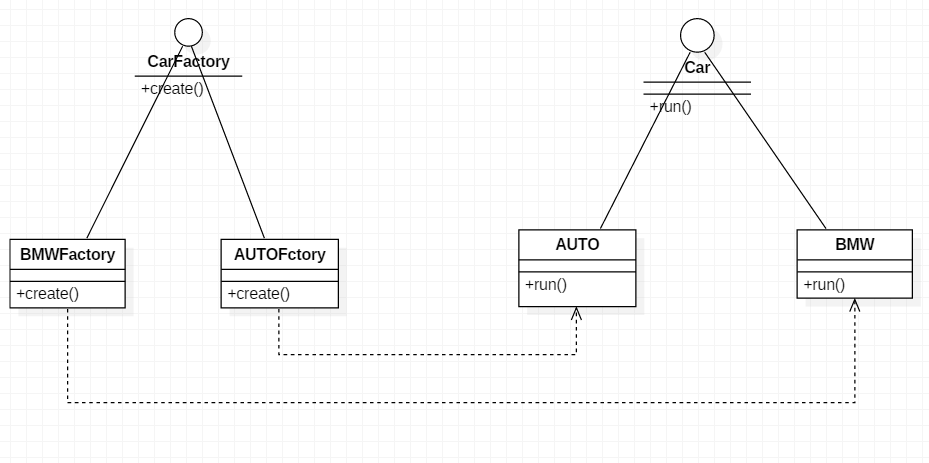
示例代码
Car接口基类1
2
3public interface Car{
void run();
}
BMW类1
2
3
4
5
6public class BMW implements Car{
public void run() {
System.out.println("BMW is run!");
}
}
AUTO类1
2
3
4
5
6public class AUTO implements Car{
public void run() {
System.out.println("AUTO is run!");
}
}
工厂抽象接口1
2
3
4public interface CarFactory<T>{
T Create();
}
BMW工厂类1
2
3
4
5
6public class BMWFactory implements CarFactor<BMW>{
public BMW create() {
return new BMW();
}
}
AUTO工厂类1
2
3
4
5public interface AUTOFactory implements CarFactor<AUTO>{
public AUTO create() {
return new AUTO();
}
}
具体调用1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public class Test{
public static void main(String []args){
AUTOFactory autoFactory = new AUTOFactory();
AUTO auto = autoFactory.create();
auto.run();
}
}
抽象工厂模式
解释
抽象工厂模式跟工厂模式最大的区别可能就是把产品再进行抽象,也就是一个抽象工厂类派生出多个具体工厂类,而具体工厂类可以生产出多个具体产品因为在现实生活中,很多产品都是一系列的,一个产品族。还按照上面的汽车的案例分析,现实生活中,你需要一台宝马,不可能说就是一种类型宝马,那宝马公司就去玩蛋蛋了,用户可能根据排量、汽车空间、稳定性、安全性各方面进行选择。所以宝马公司必须推出各个型号的子产品,例如3系和5系两款车,3系里面又包含1.5L排量的和2.0L排量的,5系同理。在实现这个需求上,我们就要对产品进行抽象,然后具体工厂写出对应的生产策略。
UML

示例代码
3系BMW抽象类1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9public abstract class BMW320i{
//排量
private float displacement;
public BMW320i(float displacement){
this.displacement = displacement;
}
public abstract void run();
//省略GET、SET
}
5系BMW抽象类1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9public abstract class BMW532i{
//排量
private float displacement;
public BMW532i(float displacement){
this.displacement = displacement;
}
public abstract void run();
//省略GET、SET
}
1.5L的BMW3系类1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public class BMW320i150 extends BMW320i{
public BMW320i150(float displacement){
super(displacement);
}
public void run() {
System.out.printf("this is a"+this.getDisplacement()+"L 320i");
}
}
2.0L的BMW3系类1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public class BMW320i200 extends BMW320i{
public BMW320i200(float displacement){
super(displacement);
}
public void run() {
System.out.printf("this is a"+this.getDisplacement()+"L 320i");
}
}
1.5L的BMW5系类1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public class BMW532i150 extends BMW532i{
public BMW532i150(float displacement){
super(displacement);
}
public void run() {
System.out.printf("this is a"+this.getDisplacement()+"L 532i");
}
}
2.0L的BMW5系类1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public class BMW532i200 extends BMW532i{
public BMW532i200(float displacement){
super(displacement);
}
public void run() {
System.out.printf("this is a"+this.getDisplacement()+"L 532i");
}
}
工厂抽象接口1
2
3
4public interface AbstractFactory {
public BMW320i createBMW320i();
public BMW532i createBMW532i();
}
1.5L抽象工厂类1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10public class BMW150Factory implements AbstractFactory{
public BMW320i createBMW320i() {
return new BMW320i150(1.5f);
}
public BMW532i createBMW532i() {
return new BMW532i150(1.5f);
}
}
2.0L抽象工厂类1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9public class BMW200Factory implements AbstractFactory {
public BMW320i createBMW320i() {
return new BMW320i200(2.0f);
}
public BMW532i createBMW532i() {
return new BMW532i200(2.0f);
}
}
具体调用1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15public class test {
public static void main(String []args){
BMW150Factory bmw150Factory = new BMW150Factory();
BMW200Factory bmw200Factory = new BMW200Factory();
BMW320i Bmw320i200 = bmw200Factory.createBMW320i();
BMW532i Bmw532i150 = bmw150Factory.createBMW532i();
Bmw320i200.run();
Bmw532i150.run();
/**结果:this is a 2.0L 320i
* this is a 1.5L 532i
*/
}
}
总结
其实不管是工厂模式还是抽象工厂模式,其目的是一致的,就是利用抽象进行解耦,也没有必要说一定要在乎用工厂还是抽象工厂,完全要根据现实需求来确定方案。

