桥接模式,组合两个对象的机器,比如我们拿画笔为例子,笔有铅笔、蜡笔、水彩笔等等,而不同的笔又有不同的颜色,如果我们用七种颜色和三只不同种类的笔的话,按照普通的逻辑,我们就需要创建二十一个类来对应不同的笔,但是有的同学就会讲了可以用工厂模式啊,对的,但是我们看待问题的角度不一样,之所以称工厂模式为创建型模式,就是用这种方法来构建出现实对象。而桥接模式是属于结构型,就是两个对象通过用一种协同的模式,让他们达到想要的逻辑。
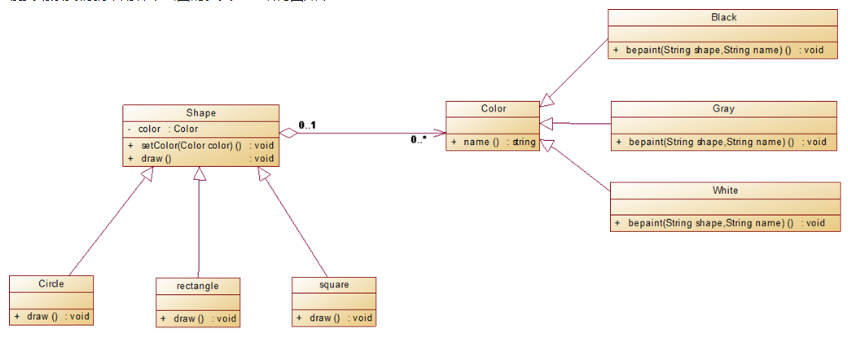
UML uml图就是banner图,不再复述
案例 还是采用简介上面的例子,用桥接模式来实现它。
首先我们创建图形抽象类,这个抽象类是关键,它里面必须包含我们实现类的接口,也就是说颜色的接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public abstract class Shape Color color; public void setColor (Color color) this .color = color; } public abstract void draw () }
然后是三个形状
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class Circle extends Shape public void draw () color.bepaint("正方形" ); } } public class Rectangle extends Shape public void draw () color.bepaint("长方形" ); } } public class Square extends Shape public void draw () color.bepaint("正方形" ); } }
颜色接口
1 2 3 public interface Color public void bepaint (String shape) }
然后是具体的颜色
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class White implements Color public void bepaint (String shape) System.out.println("白色的" + shape); } } public class Gray implements Color public void bepaint (String shape) System.out.println("灰色的" + shape); } } public class Black implements Color public void bepaint (String shape) System.out.println("黑色的" + shape); } }
最关键就看我们这个调用过程了,我们先创建白色的实现类,然后创建正方形图形,关键是融合的这一点,我们将图形上色,运用java多态的特性,设置白色的实现类,然后绘制图形的方法里再反过来调用颜色的绘制方法就实现了两个独立对象合作完成一件事情,而不是创建出一只白色的笔,再去绘制,这就区分出工厂和桥接的区别了。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class Client public static void main (String[] args) Color white = new White(); Shape square = new Square(); square.setColor(white); square.draw(); } }
--------------------------------------
文章到此就结束了,有疑问可以下方评论 --------------------------------------
赞赏支持
大部分文章都是自创,如您觉得文章不错,对您有所帮助,转载时请注明出处,也可以通过“支付宝”或“微信支付”请我喝咖啡。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
支付宝打赏二维码
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
微信打赏二维码
大部分文章都是自创,如您觉得文章不错,对您有所帮助,转载的时候请注明出处,也可以通过“支付宝”或“微信支付”请我喝咖啡。